Figure 4
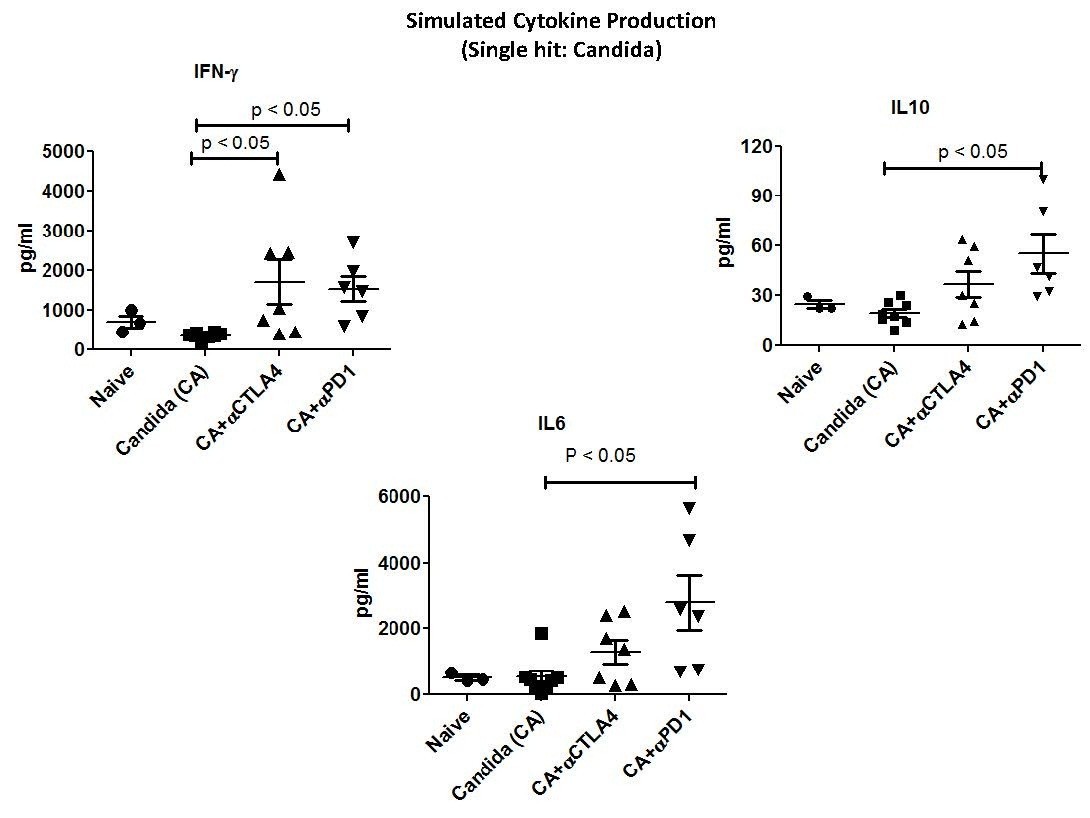
Anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 increase splenocyte cytokine production in single-hit fungal sepsis. Mice had tail vein injection of Candida and were treated with anti-PD-1 (days 2, 5 and 8 post-infection) or anti-CTLA-4 (days 4, 7 and 10 post-infection).Mice were killed and spleens harvested on day 12 post-infection.Splenocytes were prepared and stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 overnight.Supernatants were harvested and IFN-γ, IL-10 and IL-6 quantitated.Mice treated with anti-PD-1 had increases in all three cytokines compared to Candida-infected mice that were treated with saline diluent (controls) (P <0.05).Mice treated with anti-CTLA-4 had an increase in IFN-γ only (P <0.05). CD, cluster of differentiation; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; PD-1, programmed cell death 1.
